Syndesmosis Reconstruction
Stabilisation of an unstable distal tibiofibular joints (also known as high ankle sprain) using a contemporary fixation technique
The syndesmosis of the ankle is an important joint just above the ankle that is critical for ankle biomechanics. If the strong ligaments holding this joint together are injured then it can lead to significant ankle problems such as pain and arthritis in the future if left untreated [1].
In most cases surgery is recommended to stabilise this joint. The reduction is confirmed with keyhole surgery, rather than large open incisions. The ligaments are reconstructed and reinforced using a novel technique [2]
Figure 1: suture button device and ligament reconstruction for syndesmosis injury. This case also shows an ankle fracture being plated - but the syndesmosis repair can be performed in isolation
Figure 2: patient with MRI scan and weight bearing CT scan demonstrating syndesmosis instability/injury (yellow arrow)
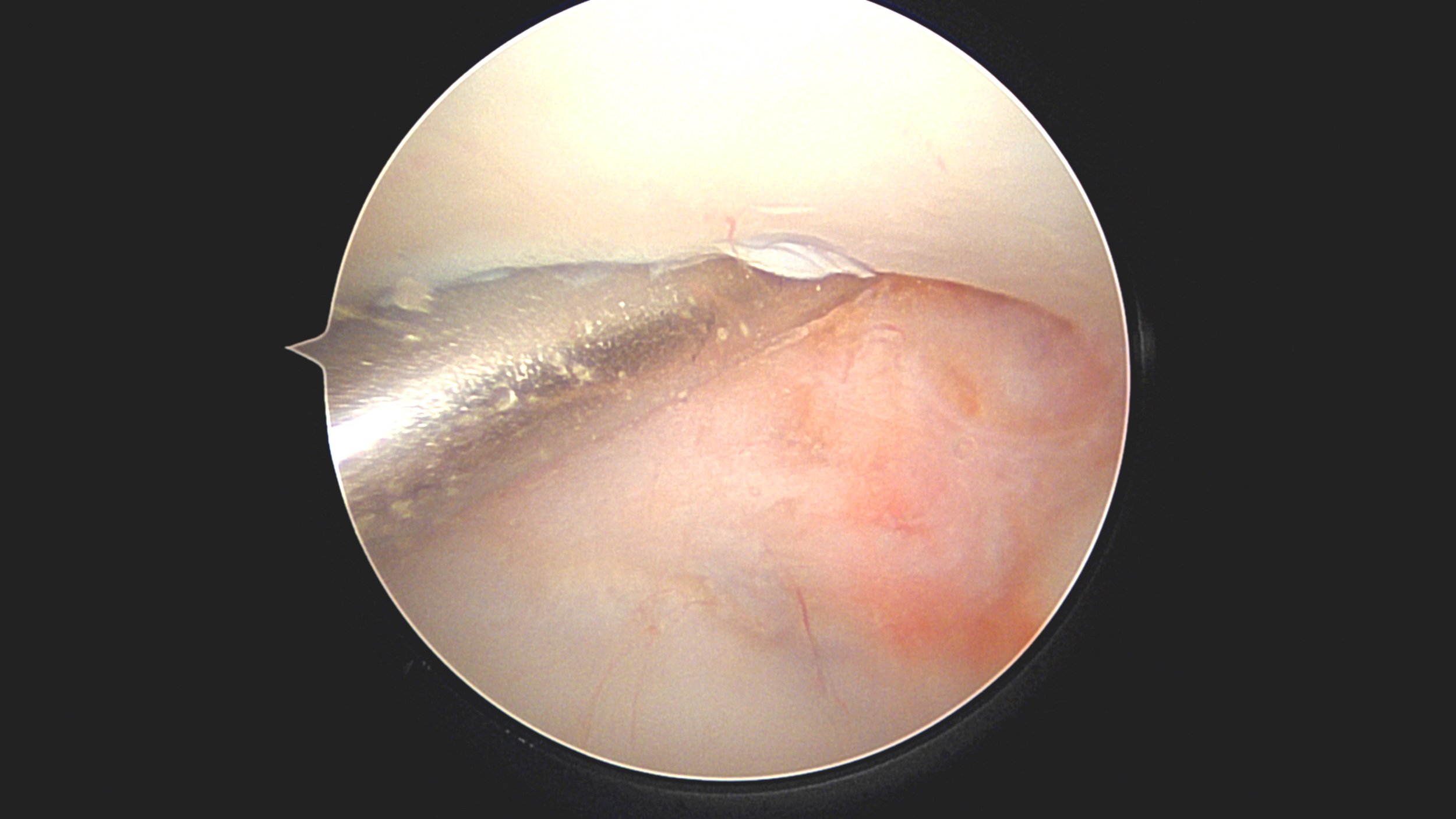
Figure 3: arthroscopic view of a patient with an unstable syndesmosis joint (positive drive through sign)
Success rates depend on the degree of injury, but most patients are satisfied with the outcome of their procedure
Post-operative plan:
Surgery is typically a day case or overnight stay
Local anaesthetic or a nerve block is administered to help with pain
0-2 weeks: elevation at home, but weight bearing in a CAMboot is allowed
2-6 weeks: full weight bearing and weaning out of the CAMboot, ongoing physiotherapy required.
6 weeks onwards: continued rehabilitation, with an aim to return to running by 10 weeks post op in routine cases.
Download post-operative care guide
Risks of surgery
Swelling, stiffness
Infection
Wound healing problems
Scar sensitivity
Failure of the procedure (ligament re-injury)
Further procedures including removal of hardware in up to 10% of patients, some patient report a stiffness/tightness in the ankle
References
Harris NJ, Nicholson G, Pountos I. Anatomical reconstruction of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament in elite athletes using InternalBrace suture tape. The Bone & Joint Journal. 2022 Jan 1;104-B(1):68–75.
Lenz CG, Urbanschitz L, Shepherd DW. Dynamic syndesmotic stabilisation and reinforcement of the antero-inferior tibiofibular ligament with internal brace. Foot (Edinb). 2023 Sep;56:102026.